Upgraded with the Anderson−Evans polyoxotungstate [TeW6O24]6− (TEW) as universal additive, the XP Screens promote protein crystallization even for most challenging targets and improve diffraction quality of protein crystals[1]. Its potential has been shown in the new protein structures of aurone synthase from Coreopsis grandiflora[2-4] (PDB code: 4Z12, 4Z13) and mushroom tyrosinase PPO4 from Agaricus bisporus[6,7] (PDB code: 4OUA). The model protein lysozyme crystallized into a new crystal form[5] (PDB code: 4PHI).
The XP Screens are TEW-optimized JBScreen Basics: 96 of the most prominent crystallization conditions complemented with TEW as "glue" for protein molecules.
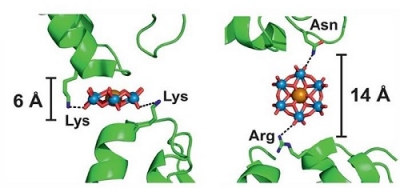
Protein-protein bridging by TEW in different orientations
Image from [1], used by courtesy of Prof. Annette Rompel, University of Vienna, Austria
Please click the arrow on the right to expand the citation list. Click publication title for the full text.
[1] Bijelic et al. (2017) Ten Good Reasons for the Use of the Tellurium-Centered Anderson-Evans Polyoxotungstate in Protein Crystallography. Acc. Chem. Res. 50:1441.
[2] Molitor et al. (2016) Aurone synthase is a catechol oxidase with hydroxylase activity and provides insights into the mechanism of plant polyphenol oxidases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 113:E1806.
[3] Molitor et al. (2016) In situ formation of the first proteinogenically functionalized [TeW6O24O2(Glu)]7- structure reveals unprecedented chemical and geometrical features of the Anderson-type cluster. Chem. Commun. 52:12286.
[4] Molitor et al. (2015) Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of latent, active and recombinantly expressed aurone synthase, a polyphenol oxidase, from Coreopsis grandiflora. Acta Cryst. F 71:746.
[5] Bijelic et al. (2015) Hen Egg-White Lysozyme Crystallisation: Protein Stacking and Structure Stability Enhanced by a Tellurium(VI)-Centred Polyoxotungstate. ChemBioChem 16:233.
[6] Mauracher et al. (2014) Latent and active abPPO4 mushroom tyrosinase cocrystallized with hexatungstotellurate(VI) in a single crystal. Acta Cryst. D 70:2301.
[7] Mauracher et al. (2014) Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of latent isoform PPO4 mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) tyrosinase. Acta Cryst. F 70:263.